ISO Certification
Key Takeaway
This comprehensive guide breaks down everything you need to know about ISO certification—from its purpose and benefits to specific standards like ISO 9001, ISO 27001, and ISO 14001. Whether you’re a small business or a large enterprise, you’ll learn who needs ISO, how to get certified, and how it can transform your operations, build trust, and open new market opportunities—all in one place.
Table of Contents










What is ISO Certification?
ISO certification is a formal recognition that a company’s processes, services, or products meet specific international standards set by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). These standards ensure quality, safety, efficiency, and consistency across industries. ISO certification acts as proof that a business operates under well-defined processes that meet globally accepted benchmarks.
Whether it’s about improving internal operations, enhancing customer satisfaction, or gaining a competitive edge, ISO certification serves as a powerful tool for businesses aiming to showcase their commitment to excellence.
Brief Background of ISO
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) was established in 1947 and is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland. It is an independent, non-governmental body made up of national standards organizations from more than 160 countries. The organization develops and publishes international standards for a wide range of industries—including manufacturing, healthcare, information technology, energy, and more.
ISO standards are developed through global consensus, ensuring they reflect practical needs and are applicable across countries and sectors.
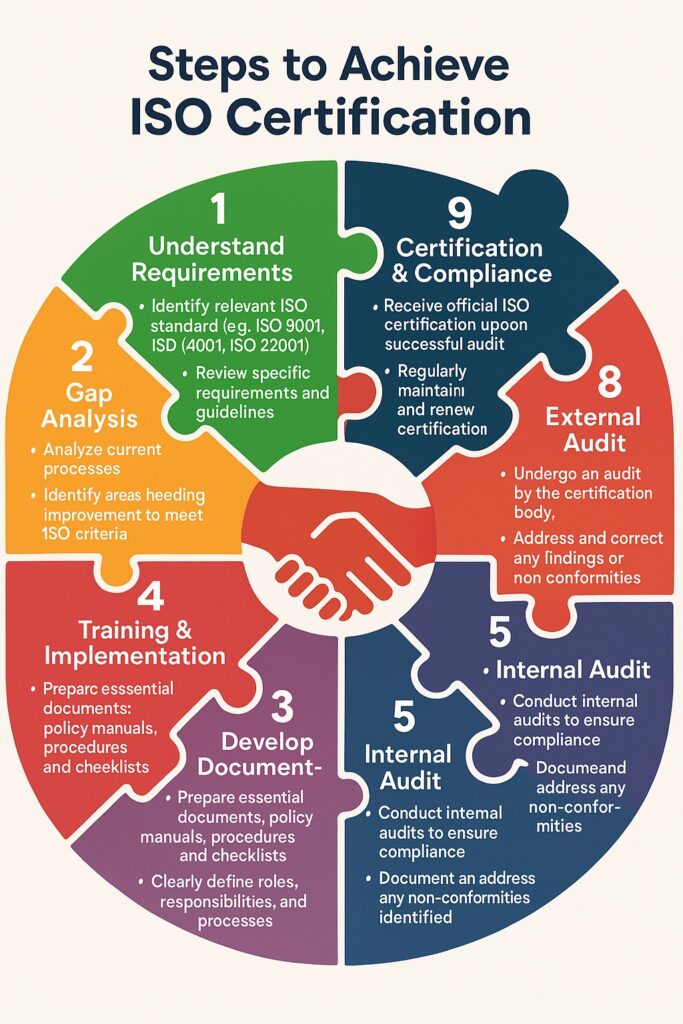
Importance in Today’s Global Market
In today’s competitive and compliance-driven global economy, ISO certification has become more than just a badge of honor—it’s often a business necessity. Here’s why:
Builds trust and credibility with customers, partners, and regulatory bodies
Improves operational efficiency by standardizing processes
Boosts international market access by meeting global trade requirements
Reduces risks and enhances decision-making through consistent quality management
Encourages continuous improvement in both products and services
Whether you’re a small business looking to expand or a large enterprise managing complex operations, ISO certification can play a crucial role in your long-term success.
ISO Certification for IT Services
In today’s digital-first world, ISO certification for IT services is more important than ever. With growing cybersecurity threats, increasing data privacy regulations, and high client expectations, businesses in the IT sector must adhere to global standards to remain competitive and trustworthy. ISO standards offer structured frameworks to manage IT processes efficiently, ensure service quality, and protect sensitive information.
ISO Standards Specific to IT
ISO 27001 – Information Security Management System (ISMS)
ISO 27001 is one of the most widely adopted standards in the IT sector. It provides a framework for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an information security management system. This standard helps organizations safeguard data confidentiality, integrity, and availability—making it especially critical for IT companies handling sensitive data or offering cloud-based solutions.
ISO 20000 – IT Service Management (ITSM)
ISO 20000 focuses on the management and delivery of IT services. It ensures that organizations follow best practices for IT service management, including incident management, problem resolution, service delivery, and continual improvement. ISO 20000 aligns closely with ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) frameworks, making it ideal for IT service providers.
Why ISO Certification Matters for IT Companies
Demonstrates data security and compliance with global standards
Improves client trust, especially when dealing with sensitive or regulated industries
Enhances operational efficiency through standardized processes
Supports bids for international projects where ISO certifications are often mandatory
Reduces risk of data breaches, service disruptions, and non-compliance penalties
Whether you’re offering cloud services, software development, or IT consulting, having relevant ISO certifications adds credibility and sets your business apart in a highly competitive market.
What Is the Use of ISO Certification?
ISO certification offers far more than just a compliance stamp—it brings real, measurable value to businesses across multiple areas. From strengthening internal processes to gaining customer confidence, ISO standards serve as a foundation for operational excellence and business growth.
Value in Operations
One of the most significant uses of ISO certification lies in optimizing internal operations. ISO standards encourage businesses to establish structured processes, reduce waste, and identify risks proactively. This leads to:
Increased efficiency
Reduced errors and rework
Better resource management
Consistent quality in outputs
For example, ISO 9001 helps companies streamline quality management systems, ensuring every department follows clearly defined procedures that lead to better outcomes.
Value in Compliance
ISO certification helps businesses stay compliant with international regulations, industry standards, and even local legal requirements. In some sectors—like healthcare, manufacturing, and IT—certification may be essential to operate or to participate in tenders.
It acts as a ready-made framework that aligns with many regulatory requirements, minimizing the risk of penalties and legal issues.
Value in Marketing
Holding an ISO certification is a powerful marketing tool. It tells potential customers and partners that your company meets global standards. This can:
Increase your chances of winning contracts and RFPs
Build stronger client relationships
Set you apart from uncertified competitors
Support expansion into international markets
ISO logos or certification marks (when used correctly) also add trust elements to websites, proposals, and promotional materials.
Value in Trust & Reputation
Trust is the backbone of any successful business. ISO certification assures customers, stakeholders, and investors that your organization follows recognized standards for quality, safety, and reliability.
It boosts your reputation by showing that you’re committed to continuous improvement, transparency, and customer satisfaction.
Who Needs ISO Certification?
ISO certification is relevant for organizations of all sizes and across virtually every industry. Whether you’re a startup aiming for credibility or a multinational company seeking operational excellence, ISO standards offer structured frameworks that can help you grow, scale, and compete globally.
Industries & Sectors
ISO certification is widely applicable and often essential in the following industries:
Manufacturing – Ensures quality control, safety, and process efficiency
Information Technology – Secures data, manages IT services, and protects systems (ISO 27001, ISO 20000)
Healthcare – Promotes patient safety, service quality, and regulatory compliance
Construction & Engineering – Improves safety, environmental management, and risk reduction
Education & Training – Enhances service delivery and student satisfaction
Logistics & Supply Chain – Boosts reliability, traceability, and customer confidence
Food & Hospitality – Ensures food safety, hygiene, and consistent quality (e.g., ISO 22000)
Many public tenders, contracts, and B2B partnerships now require ISO certification as a prerequisite, especially in regulated industries.
Small Businesses vs Enterprises
Small Businesses
For small businesses, ISO certification builds credibility and opens doors to new opportunities. It shows potential clients that even with limited size, your business follows internationally recognized best practices. It also helps structure your internal processes early, which can make growth smoother and more sustainable.
Enterprises
Larger organizations use ISO certification to ensure consistency across departments, locations, or even global operations. It’s a key tool for risk management, customer satisfaction, and compliance—especially when dealing with international clients, regulatory bodies, or complex supply chains.
Who Is Eligible for an ISO?
One of the most common misconceptions is that ISO certification is only for large or specialized organizations. In reality, any organization—big or small, private or public, product-based or service-based—can apply for ISO certification. What matters most is the willingness to implement and maintain systems that meet the requirements of the chosen ISO standard.
Eligibility Criteria
There is no fixed list of eligibility requirements for ISO certification. Instead, the eligibility depends on:
The specific ISO standard you are applying for (e.g., ISO 9001 for quality management, ISO 27001 for information security, etc.)
Your commitment to aligning your internal processes with the requirements of that standard
A functioning management system in place, even if it’s informal or not yet fully documented
The ability to demonstrate evidence of process control, continuous improvement, and compliance
Organizations from any industry or location are eligible, as long as they are ready to undergo the necessary implementation and audit process.
Required Documentation
While documentation may vary slightly depending on the standard, some common documents required for ISO certification include:
Company profile and scope of activities
Process flowcharts or SOPs (Standard Operating Procedures)
Quality or management policy documents
Internal audit records
Risk assessment and mitigation plans
Corrective action records
Training records and employee responsibilities
Customer feedback and complaints log
For example, in ISO 9001, a Quality Management System (QMS) with documented procedures and a quality manual is essential. In ISO 27001, you’ll need policies for information security, access control, asset management, and more.
Even if your company is just starting, you can gradually build the systems required and become eligible for ISO certification. Many businesses work with consultants or certification bodies to help them prepare the necessary documentation and align their processes accordingly.
What Is the Main Purpose of ISO Certification?
The main purpose of ISO certification is to establish trust by ensuring that an organization’s systems, processes, or products meet internationally recognized standards. ISO certification demonstrates a company’s commitment to quality, consistency, and continuous improvement—qualities that are essential for long-term success in any industry.
Key Purposes of ISO Certification
Enhancing Quality and Efficiency
- At its core, ISO certification helps businesses create efficient, repeatable processes. This leads to improved product or service quality, fewer errors, reduced waste, and better use of resources.
Building Customer Confidence
- When customers see that a company is ISO certified, it builds confidence. It shows that the organization follows best practices, maintains high standards, and puts customer satisfaction at the forefront.
Facilitating Compliance and Risk Management
- Many ISO standards include elements of regulatory compliance and risk mitigation. Certification helps businesses proactively identify and address potential issues before they become serious problems.
Encouraging Continuous Improvement
- ISO standards promote a culture of ongoing evaluation and improvement. Certified businesses are expected to regularly assess their processes, identify areas for enhancement, and take corrective action.
Opening Market Opportunities
- ISO certification can be a gateway to new markets—both domestic and international. It’s often a requirement for bidding on government contracts, forming B2B partnerships, or entering regulated industries.
In summary, the purpose of ISO certification goes beyond just meeting requirements—it’s about building a better, more reliable, and more competitive organization that’s prepared for the future.
Is ISO Legally Required?
One of the most frequently asked questions about ISO certification is whether it is a legal requirement. The short answer is: in most cases, ISO certification is not legally required, but it can be a powerful tool for demonstrating compliance and credibility.
Compliance vs Optional
ISO certification is typically voluntary. Most ISO standards, such as ISO 9001 (quality management) or ISO 14001 (environmental management), are not mandated by law. Instead, they are frameworks designed to help organizations improve efficiency, meet customer expectations, and enhance overall performance.
However, while not legally enforced, ISO certification is often required by customers, partners, or industry regulators as a condition for doing business. For example, many government and corporate contracts require ISO-certified suppliers.
So, although it’s technically optional, ISO certification often becomes essential in practice if a business wants to compete in certain markets or industries.
Industry-Specific Mandates
In some sectors, ISO certification aligns so closely with regulatory compliance that it becomes a de facto requirement. Here are a few examples:
Healthcare & Medical Devices – ISO 13485 certification is often required to meet medical regulations.
Information Technology – ISO 27001 is increasingly expected to comply with data protection laws and cybersecurity requirements.
Food Industry – ISO 22000 is crucial for demonstrating food safety standards.
Automotive & Aerospace – Industry-specific ISO standards (like IATF 16949 for automotive) are often mandatory for suppliers.
In such industries, certification may not be enforced by law, but without it, companies may be barred from operating or lose access to major business opportunities.
In conclusion, ISO certification is usually not a legal obligation, but depending on your industry, it may be necessary to stay competitive, compliant, and trusted.
What Are the 7 Principles of ISO?
The foundation of most ISO management system standards—especially ISO 9001 (Quality Management System)—is built upon seven quality management principles. These principles serve as a guide for organizations to improve performance, deliver value, and maintain customer trust.
Here’s a brief overview of each:
Customer Focus
The primary goal of quality management is to meet customer requirements and strive to exceed customer expectations. Organizations should understand their customers’ needs and aim for long-term satisfaction and loyalty.
Leadership
Strong leadership provides a clear vision and direction. When leaders at all levels are aligned with the organization’s purpose and values, it promotes a unified culture and drives engagement.
Engagement of People
People at all levels are essential to the success of an organization. Involving employees, empowering them, and recognizing their contributions boosts productivity and innovation.
Process Approach
Managing activities as processes leads to more predictable and consistent results. This approach helps streamline operations, eliminate waste, and improve performance.
Improvement
Continual improvement should be a permanent goal of every organization. ISO encourages a culture of innovation, learning, and adaptation to stay competitive and resilient.
Evidence-Based Decision Making
Effective decisions are based on the analysis of data and information. Organizations should rely on facts, trends, and performance metrics to make informed choices and minimize risks.
Relationship Management
An organization’s success depends on strong relationships with interested parties such as suppliers, partners, customers, and other stakeholders. Building trust and collaboration leads to long-term success.
These principles are not just theoretical—they are practical guidelines that support the structure of any ISO-certified management system. Organizations that apply them consistently are more likely to achieve sustainable results and maintain compliance.
ISO Green Certification
In today’s world, where environmental responsibility is becoming a top priority, many organizations are pursuing ISO green certification to showcase their commitment to sustainability. These certifications focus on minimizing environmental impact, improving resource efficiency, and complying with eco-friendly regulations.
The most prominent among them is ISO 14001, but several other ISO standards also contribute to green initiatives.

ISO Standard | Focus Area | Who It’s For |
ISO 14001 | Environmental Management System (EMS) | All industries aiming to reduce environmental impact |
ISO 14064 | Greenhouse Gas Emissions (GHG) Management | Organizations tracking and reducing carbon footprints |
ISO 50001 | Energy Management Systems | Companies wanting to improve energy performance |
ISO 20121 | Sustainable Event Management | Event planners, venues, and hospitality providers |
ISO 26000 | Social Responsibility (guidance only) | Businesses seeking ethical, environmental best practices |
Why ISO Green Certifications Matter
Meet global sustainability goals
Reduce energy, waste, and operational costs
Improve reputation and brand image
Gain trust from eco-conscious clients and regulators
Prepare for future environmental regulations
Obtaining a green ISO certification not only helps the planet but also gives your organization a competitive advantage in a market that’s increasingly focused on environmental and social responsibility.
ISO 27001 Certification
ISO 27001 is the internationally recognized standard for Information Security Management Systems (ISMS). It provides a framework for managing sensitive company and customer information, ensuring it remains secure, confidential, and accessible only to authorized individuals.
With increasing cyber threats and data privacy concerns, ISO 27001 certification has become essential for businesses that handle any form of sensitive data.
What It Is
ISO 27001 outlines best practices for identifying, managing, and reducing risks to information security. It focuses on:
Risk assessment and treatment
Access control policies
Incident response plans
Secure communication and data handling
Continuous monitoring and improvement
It is not just about IT—it applies to people, processes, and technology involved in securing information.
Who Needs It
ISO 27001 certification is ideal for:
IT service providers and software companies
Cloud and data storage companies
Banks and financial institutions
Healthcare organizations handling patient data
Educational institutions managing student records
Any business that processes or stores confidential customer data
Even small businesses and startups benefit from ISO 27001, especially if they work with enterprise clients or in highly regulated industries.
Benefits
Builds trust with clients and stakeholders
Helps comply with data protection regulations (like GDPR)
Reduces the risk of data breaches and cyber attacks
Improves incident response readiness
Enhances your company’s reputation and credibility
Creates a culture of security awareness and responsibility
ISO 45001 Certification
ISO 45001 is the international standard for Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems (OHSMS). It helps organizations create safer working environments by proactively identifying and managing risks that can lead to work-related injuries, illnesses, or accidents.
This certification replaces the older OHSAS 18001 and is now the globally accepted standard for health and safety at the workplace.
What It Covers
ISO 45001 focuses on:
Identifying workplace hazards
Implementing controls to reduce risks
Promoting employee well-being
Complying with health & safety regulations
Continuous improvement of safety practices
It applies to all organizations, regardless of size, industry, or location.
Who Needs ISO 45001?
This certification is highly relevant for:
Construction and engineering companies
Manufacturers and factories
Logistics, warehousing, and transportation firms
Healthcare providers
Oil & gas and high-risk industries
Any organization looking to protect workers and improve safety culture
Key Benefits
Prevents workplace incidents and injuries
Improves employee morale and productivity
Reduces legal liabilities and compensation claims
Enhances compliance with safety laws
Boosts reputation among clients, regulators, and partner
ISO 9001 Certification
ISO 9001 is the world’s most widely recognized standard for Quality Management Systems (QMS). It provides a structured approach to consistently deliver products and services that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
This standard is applicable to businesses of all types and sizes, making it a core ISO certification across industries.
What It Focuses On
ISO 9001 emphasizes:
Process efficiency and standardization
Customer satisfaction
Continuous improvement
Risk-based thinking
Strong internal leadership and employee involvement
It encourages a culture where quality is built into every stage of operations—from planning to production to customer service.
Who Should Get ISO 9001?
Manufacturing companies
Service-based businesses
Healthcare and education providers
Government contractors and suppliers
Any organization aiming to improve performance and customer trust
It is especially valuable for businesses looking to expand globally or enter into partnerships where quality assurance is a key requirement.
Key Benefits
Delivers consistent quality and fewer errors
Enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty
Improves process control and efficiency
Opens doors to new markets and opportunities
Builds a strong foundation for scaling operations
ISO 14001 Certification
ISO 14001 is the international standard for Environmental Management Systems (EMS). It provides a framework for organizations to manage their environmental responsibilities in a systematic and sustainable way.
With growing environmental concerns and strict regulations, ISO 14001 helps businesses reduce their environmental footprint while improving operational efficiency.
What It Focuses On
ISO 14001 emphasizes:
Reducing waste and pollution
Efficient use of energy and natural resources
Compliance with environmental laws and regulations
Setting and achieving environmental objectives
Continuous monitoring and improvement
It follows the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle, encouraging ongoing enhancement of environmental performance.
Who Should Get ISO 14001?
Manufacturing and industrial companies
Construction and engineering firms
Energy and utility providers
Food production and packaging businesses
Any organization seeking to improve sustainability
It is particularly valuable for businesses that want to align with environmental goals, improve public image, and reduce costs associated with waste or inefficiency.
Key Benefits
Demonstrates commitment to sustainability
Reduces environmental risks and costs
Enhances regulatory compliance
Improves stakeholder trust and reputation
Supports access to green markets and eco-conscious clients
How to Get ISO Certification for a Training Institute
For training institutes, ISO certification (usually ISO 9001) ensures the quality of educational services. Here’s a quick step-by-step:
- Identify the right standard (e.g., ISO 9001 for quality, ISO 21001 for educational organizations)
- Conduct a gap analysis against the standard
- Develop documentation like SOPs, training manuals, feedback systems
- Implement and train staff
- Conduct internal audits
- Choose a certification body and go through the external audit
Certification helps build trust, attract students, and improve course quality.
ISO Accreditation vs Certification


ISO Accreditation vs Certification
This typically refers to ISO 9001 and focuses on maintaining consistent quality in services or products.
Key Benefits:
Enhances customer satisfaction
Boosts efficiency and accountability
Opens up new business opportunities
Basic Implementation:
- Analyze your current quality system
- Align processes with ISO 9001 requirements
- Train staff and maintain documentation
- Go for external certification audit
ISO Quality Management Certification
This typically refers to ISO 9001 and focuses on maintaining consistent quality in services or products.
Key Benefits:
- Enhances customer satisfaction
- Boosts efficiency and accountability
- Opens up new business opportunities
Basic Implementation:
- Analyze your current quality system
- Align processes with ISO 9001 requirements
- Train staff and maintain documentation
- Go for external certification audit
Benefits of ISO Certification to an Organization
Builds brand trust
Improves internal efficiency
Reduces operational risk
Opens doors to global markets
Enhances customer satisfaction
Supports compliance with regulations
Encourages continuous improvement

Many companies report improved performance, higher customer retention, and greater competitiveness after getting ISO certified.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How long does it take to get ISO certified?
With KCS, ISO certification can be completed in as little as 2 working days, depending on the organization’s readiness and documentation status. Timelines may vary based on the chosen ISO standard and scope of work.
2. How much does ISO certification cost?
Costs vary, but with KCS, ISO certification starts at just AED 2,250 (around $607.50 USD)—making it an affordable option for businesses of all sizes. Prices may vary based on the ISO type and company scope.
3. Can a company have multiple ISO certifications?
Yes. Many companies hold multiple ISO certifications, such as ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environment), and ISO 27001 (information security), depending on their business scope.
4. What are the risks of not having ISO certification?
Without ISO certification, companies may face:
- Limited market access
- Lower client trust
- Operational inefficiencies
- Compliance challenges in regulated industries
5. How often should ISO be renewed?
ISO certifications are typically valid for 3 years, with surveillance audits every year to ensure continued compliance.
Conclusion
ISO certification is more than just a document—it’s a strategic step toward operational excellence, customer trust, and long-term business growth. Whether you’re a startup, training provider, or enterprise-level organization, aligning your processes with international standards helps you stay competitive and credible in today’s global market.
From popular certifications like ISO 9001 for quality management, ISO 27001 for information security, and ISO 14001 for environmental management, to industry-specific standards such as ISO 45001 (occupational health & safety) and ISO 22000 (food safety), there are many ISO standards designed to fit your exact business needs.



